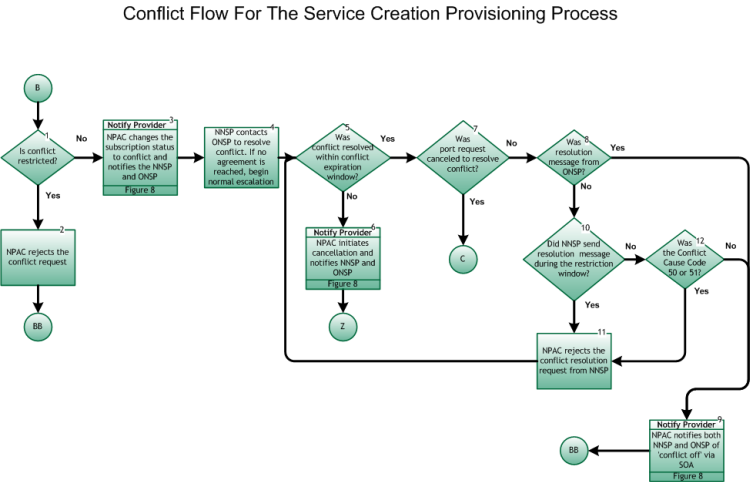
Step 1: Is conflict restricted?
- The conflict flow is entered through the Provisioning process flow (Main Porting Flow) through tie point (B), Figure 6, when the ONSP enters a concurrence flag of “No”, and designates a conflict cause code.
- Conflict is restricted (i.e., SV may not be placed into conflict by the ONSP) if one of the following:
- The ONSP previously placed the subscription into conflict, or
- The ONSP never sent a create message for this subscription, or
- The request was initiated too late:
- For wireline Simple Ports, the request was initiated after the tunable time (Simple Port Conflict Restriction Window, current value of 9:00pm in the predominate time zone of the NPAC region where the number is being ported) one Business Day before the Due Date and T2 Timer (Final Concurrence Window tunable parameter) has expired.
- For wireline Non-Simple Ports, the request was initiated after the tunable time (Conflict Restriction Window, current value of 12:00) one Business Day before the Due Date and T2 Timer (Final Concurrence Window tunable parameter) has expired.
- For wireless SPs using short timers for this SV, the conflict request is not restricted and can be initiated up to the time the port is activated.
- If Yes, go to Step 2.
- If No, go to Step 3.
Step 2: NPAC rejects the conflict request
- NPAC notifies SP of rejection.
- The porting process resumes as normal, proceeding to the Provisioning process flow (Main Porting Flow) at tie point BB, Figure 6.
Step 3: Notify Provider – NPAC changes the subscription status to conflict and notifies NNSP and ONSP
- For the notification process, refer to Inter-Service Provider LNP Operations Flows – Reseller/Interconnected VoIP Provider/Type 1 Notification, Figure 8.
- Both SPs take appropriate action related to internal work orders.
- SVs may be modified while in the conflict state (e.g., due date), by either the NNSP or ONSP.
Step 4: NNSP contacts ONSP to resolve conflict. If no agreement is reached, begin normal escalation
- The escalation process is defined in the inter-company agreements between the involved service providers.
Step 5: Was conflict resolved within conflict expiration window?
- From the time an SV is placed in conflict, there is a tunable window (Conflict Expiration Window, current value of 30-calendar day limit after the due date) after which it is removed from the NPAC database. If it is resolved within the tunable window, go to Step 7; if not, the subscription request will “time out” and go to Step 6.
Step 6: Notify Provider – NPAC initiates cancellation and notifies NNSP and ONSP
- For the Notification process, refer to Inter-Service Provider LNP Operations Flows – Reseller/Interconnected VoIP Provider/Type 1 Notification, Figure8.
- Both SPs take appropriate action related to internal work orders.
Step 7: Was port request canceled to resolve conflict?
- Conflict resolution initiates one of two actions: 1) cancellation of the subscription, or 2) resumption of the service creation provisioning process. If the conflict is resolved by cancellation of the subscription, then proceed to the Cancellation Flows for Provisioning Process through tie point C, Figure 12. If the conflict is otherwise resolved, go to Step 8.
Step 8: Was resolution message from ONSP?
- If Yes, go to Step 9.
- If No, go to Step 10
Step 9: Notify Provider – NPAC notifies the NNSP and ONSP of “conflict off” via SOA
- For the Notification process, refer to Inter-Service Provider LNP Operations Flows – Reseller/Interconnected VoIP Provider/Type 1 Notification, Figure 8.
- NPAC notifies both SPs of the change in SV status. The porting process resumes as normal, proceeding to the Provisioning process flow (Main Porting Flow) at tie point BB, Figure 6.
Step 10: Did NNSP send resolution message during the restriction window?
- If conflict was resolved within tunable business hours (current values of six hours for wireline-involved Non-Simple Ports [Long Conflict Resolution New Service Provider Restriction], two hours for wireline-involved Simple Ports [Medium Conflict Resolution New Service Provider Restriction], and six hours for wireless [Short Conflict Resolution New Service Provider Restriction] ), only the ONSP may notify NPAC of “conflict off”. If conflict was resolved after tunable hours, either the NNSP or ONSP may notify NPAC of “conflict off”.
- In order for the porting process to continue at least one SP must remove the SV from conflict.
- If Yes, go to Step 11.
- If No, go to Step 12.
Step 11: NPAC rejects the conflict resolution request from NNSP
- NPAC sends an error to the NNSP indicating conflict resolution is not valid at this point in time.
- Return to Step 5.
Step 12: Was the Conflict Cause Code 50 or 51?
- If Yes, go to Step 11.
- If No, go to Step 9
Step 13: End